Using Github
Learn how to add your team to your GitHub Organization account, fork and clone the repos to their VMs and get them ready to start their coding tasks right away.
resource:
github_adduser:
my-user:
username : alisonheart
organization : my-company
repos : [my-web-app, my-other-app]
teams : [Developers]
title : key used in koding-vms
SSHKey : "ssh-rsa AAAVSVSDFSdfsdfsdfsdfs..."
Above script will:
- Add Alison to my-company organization
- Fork my-web-app and my-other-app repo to Alison’s account
- Add Alison to Developers team
- Add Alison’s SSH keys to Alison’s GitHUb account so that Alison can pull & push from this repository right away!**
Full Stack
# This stack installs git and pulls code base from GitHub
# The stack uses the private key listed in the Private Variables section
koding:
userInput:
PrivateKey: textarea # Ask user to input their private key
PublicKey: textarea # Ask user to input their public key
provider:
aws:
access_key: '${var.aws_access_key}'
secret_key: '${var.aws_secret_key}'
github:
organizationKey : ${var.custom_github_org_key} # Prepare your organization key and use here
userKey : ${var.userInput_github_userkey} # Ask user to prepare and input their Github personal access token
resource:
github_adduser:
user:
username : ${var.userInput_github_username} # Ask user to enter their github username
organization : my-company # Your organization name on github
repos : [bricks4] # Repositories that will be forked to the user
teams : [Devs] # Teams that the user will be added as a member or admin
title : key used in koding-vms # Title of the key that will be inserted into users github account
SSHKey : ${var.userInput_PublicKey} # User's public key that will be inserted along with the title
aws_instance:
dev:
instance_type: t2.nano
user_data: |
export GITHUB_USERNAME=${var.userInput_github_username}
export GITHUB_PROJECT=bricks4
export USER_NAME=${var.koding_user_username}
export USER_HOME=/home/$USER_NAME
mkdir -p $USER_HOME/.ssh
echo "${var.userInput_PrivateKey}" >> $USER_HOME/.ssh/id_rsa # insert private key so that this vm can access the forked repo
echo "${var.userInput_PublicKey}" >> $USER_HOME/.ssh/id_rsa.pub # insert public key
chown $USER_NAME:$USER_NAME $USER_HOME/.ssh
chown $USER_NAME:$USER_NAME $USER_HOME/.ssh/id_rsa
chmod 600 $USER_HOME/.ssh/id_rsa # make sure file permissions are set correctly
apt-get update
apt-get install -y git-core # install git
# since user will not be interacting with this bash execution,
# we don't want bash to stop and ask "do you want to continue yes/no"
echo "Host github.comn User gitn IdentityFile $USER_HOME/.ssh/id_rsan StrictHostKeyChecking no" >> $USER_HOME/.ssh/config
# clone the repository with the correct user (stack script is run as root)
su $USER_NAME -c "git clone [email protected]:mars-org/$GITHUB_PROJECT $USER_HOME/$GITHUB_PROJECT"
# add the master repository as upstream
su $USER_NAME -c "git remote add -f upstream [email protected]:mars-org/$GITHUB_PROJECT"
# Voila! now user can do
# git pull origin master -> this will pull from github.com/alison/my-web-app
# git pull origin upstream -> this will pull from github.com/my-company/my-web-app
# CONGRATULATIONS - You are now set up to use your github repo in your dev environment!
Steps Overview:
- Create or use an admin user on GitHub
- Generate SSH keys and personal access token
- Add
githubas provider to the stack - Use
github_addusersection to add the user to your organization & team, and to fork the repo to user GitHub account - Get user’s SSH keys as inputs and add them to his Koding VM to be able to push/pull from the repo
- Clone the repo to user’s VM
This guide is intended for the team admin, the one creating the stack for the team. Developers will be able to build their VMs and start developing, editing & committing directly.
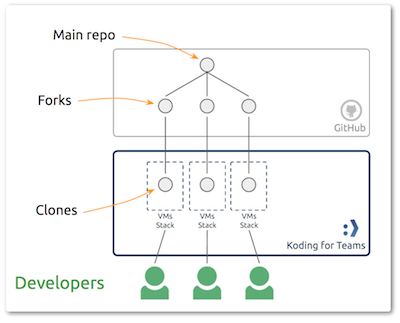
Step 1 - GitHub:
Login with an admin/master GitHub user account. Use the account to login to Github and create or pull the project which your developers will be working on, the “Main repo” and setup Github organization and team.
Step 2 - SSH Keys & Token:
- Using the admin/master user create SSH key
- Add the PUBLIC KEY to the admin GitHub account, for steps click here
- Create a personal access token, and check scopes
repo, admin:public_key, user
Step 3 - Create the stack:
Use Input values, input types section and variables to ask for user input and store required values which will be later used in the stack. The syntax var.userInput_VARIABLE_NAME can be used in your stack file to define a user input. When a developer clicks build stack, a window will open to ask them for the variable value.
Using bash commands under the user_date section, you can also define variables to use in your commands, all commands there are pure bash.
- In the
userInputsection we declare the user input type for our variables, we use textarea forPrivateKey&PublicKeyto provide more input space for the user. Hint: You can also use password type for passwords input if required
userInput:
PrivateKey: textarea
PublicKey: textarea
-
In the
provider section, after the aws keys section, we declare the github user keys. And define their values as user input values. The syntax var.userInput_VARIABLE_NAME can be used in your stack file to define a user input. In this section the stack template will store the admin/main account key “organizationKey” and the developer/user account “user-key”organizationKeyis the main/admin user access tokenuserKeyis the the developer/user access token (they should generate their access token from GitHub)
provider:
aws:
access_key: '${var.aws_access_key}'
secret_key: '${var.aws_secret_key}'
github:
organizationKey : ${var.custom_github_org_key}
userKey : ${var.userInput_github_userkey}
- In the
resourcessection, the stack template will add the user using the user and repo information.usernamedeveloper GitHub username defined as user inputorganizationGitHub OrganizationreposGitHub repository names the user could forkteamsGitHub organization teams the user will be addedtitletitle for SSHKeySSHKeydeveloper Public Key
In our case, the organization “mars-org” has a team called “Devs” working on the “bricks4” repo (teams and repos can take more than 1 argument)
resource:
github_adduser:
user:
username : ${var.userInput_github_username}
organization : mars-org
repos : [bricks4]
teams : [Devs]
title : key used in koding-vms
SSHKey : ${var.userInput_PublicKey}
- In the
user_datasection we start by using variables to store some of the data the user entered to clone the repo later
user_data: |-
export GITHUB_USERNAME=${var.userInput_github_username}
export GITHUB_PROJECT=bricks4
export USER_NAME=${var.koding_user_username}
export USER_HOME=/home/$USER_NAME
- Create .ssh directory:
mkdir -p $USER_HOME/.ssh
- Store developer’s public and private keys:
echo "${var.userInput_PrivateKey}" > $USER_HOME/.ssh/id_rsa
echo "${var.userInput_PublicKey}" > $USER_HOME/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
- Change the
.sshfolder andid_rsafile permissions to user account and group
chown $USER_NAME:$USER_NAME $USER_HOME/.ssh
chown $USER_NAME:$USER_NAME $USER_HOME/.ssh/id_rsa
chmod 600 $USER_HOME/.ssh/id_rsa
- Update packages list and install git:
apt-get update
apt-get install -y git-core
- Setup the config file. By default, SSH will prompt you if it should add a remote server to your known hosts. So it will require an answer (yes/no) if the host key received from the remote server does not match the one found in the known_hosts file. Since the developers will be building new VM(s) using the stack you are creating, you may want to automate the process without prompts. i.e. configure SSH to add hosts to the known_hosts file automatically by setting
StrictHostKeyCheckingtono. Please be aware that this can have security implications, so make sure you and your developers are aware of this fact.
echo "Host github.com\n User git\n IdentityFile $USER_HOME/.ssh/id_rsa\n StrictHostKeyChecking no" >> $USER_HOME/.ssh/config
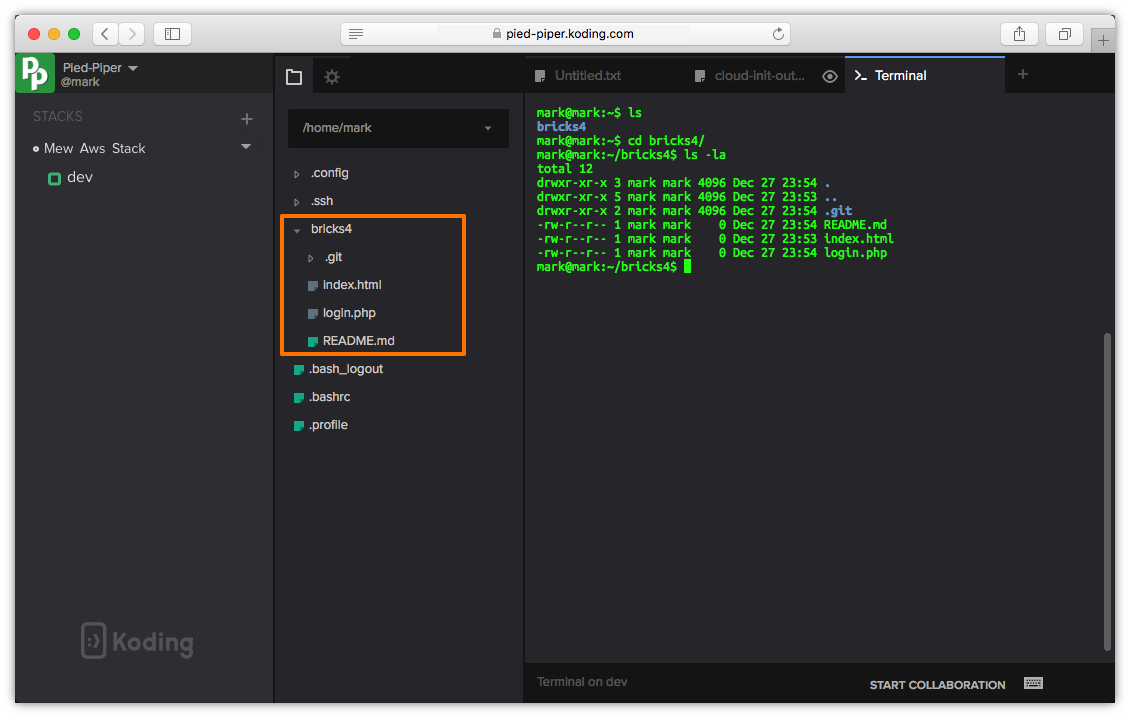
- Clone the repo and add main repo as remote
su $USER_NAME -c "git clone [email protected]:mars-org/$GITHUB_PROJECT $USER_HOME/$GITHUB_PROJECT"
su $USER_NAME -c "git remote add -f upstream [email protected]:mars-org/$GITHUB_PROJECT"
Step 4 - Let your developers know!
Edit the Readme message to educate your developers and save even more time. Let them know the steps they need to take with a simple message.
You’ll be asked to provide the following
- Enter your Github username
- Enter your Github Key click here to generate one
- Select these in the token while generating key: repo, admin:public_key, user
- Enter your private and public ssh key
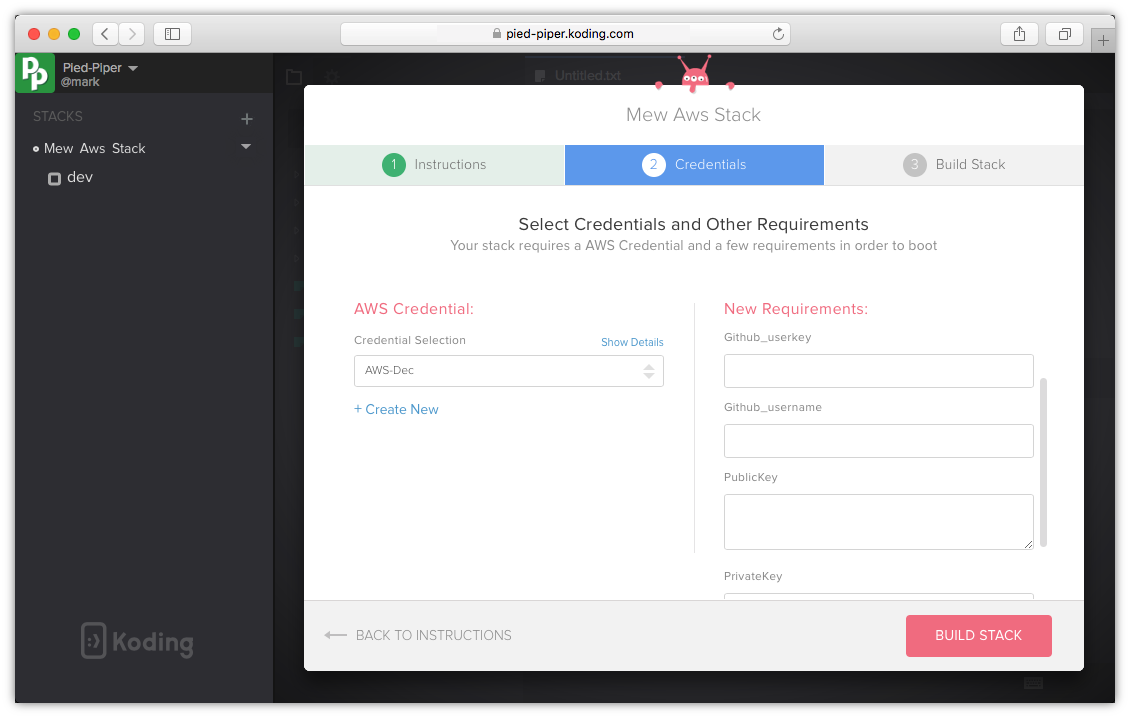
Step 5 - Invite your developers:
Invite your developers to your Koding for teams group and ask them to login and build their stack. Once they login and build the stack they will be prompted to enter their GitHub username then their VM will continue to build successfully with the code base pulled and ready for commits. On the admin GitHub account, he should be able to see the developers accounts created successfully.
Happy Koding!